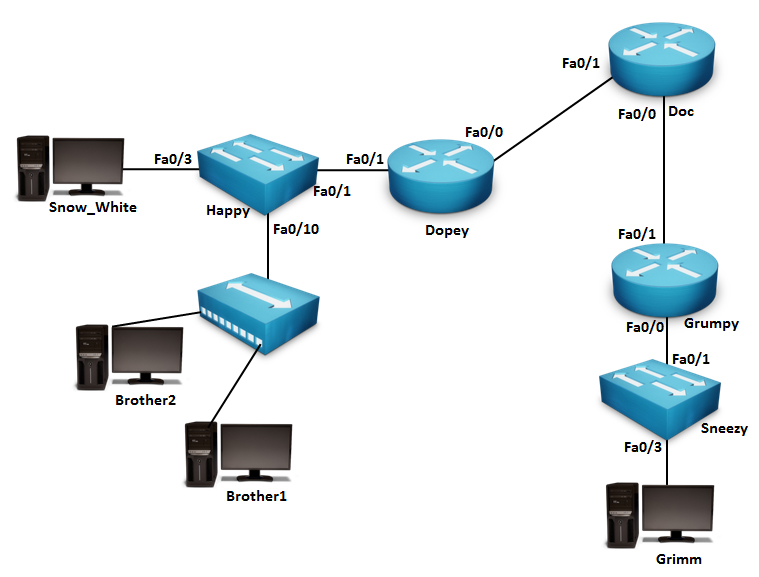
OSPF
The OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) protocol is one of a family of IP Routing protocols, and is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) for the Internet, used to distribute IP routing information throughout a single Autonomous System (AS) in an IP network.
The OSPF protocol is a link-state routing protocol, which means that the routers exchange topology information with their nearest neighbors. The topology information is flooded throughout the AS, so that every router within the AS has a complete picture of the topology of the AS. This picture is then used to calculate end-to-end paths through the AS, normally using a variant of the Dijkstra algorithm. Therefore, in a link-state routing protocol, the next hop address to which data is forwarded is determined by choosing the best end-to-end path to the eventual destination.
Each OSPF router distributes information about its local state (usable interfaces and reachable neighbors, and the cost of using each interface) to other routers using a Link State Advertisement (LSA) message. Each router uses the received messages to build up an identical database that describes the topology of the AS.
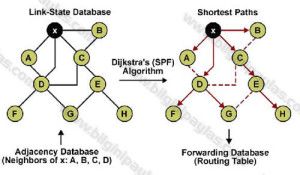
From this database, each router calculates its own routing table using a Shortest Path First (SPF) or Dijkstra algorithm. This routing table contains all the destinations the routing protocol knows about, associated with a next hop IP address and outgoing interface.
- The protocol recalculates routes when network topology changes, using the Dijkstra algorithm, and minimises the routing protocol traffic that it generates.
- It provides support for multiple paths of equal cost.
- It provides a multi-level hierarchy (two-level for OSPF) called “area routing,” so that information about the topology within a defined area of the AS is hidden from routers outside this area. This enables an additional level of routing protection and a reduction in routing protocol traffic.
- All protocol exchanges can be authenticated so that only trusted routers can join in the routing exchanges for the AS.
LSA types :
- Type 1 – Router LSA: The Router LSA is generated by each router for each area it is located. In the link-state ID you will find the originating router’s ID.
- Type 2 – Network LSA: Network LSAs are generated by the DR. The link-state ID will be the router ID of the DR.
- Type 3 – Summary LSA: The summary LSA is created by the ABR and flooded into other areas.
- Type 4 – Summary ASBR LSA: Other routers need to know where to find the ASBR. This is why the ABR will generate a summary ASBR LSA which will include the router ID of the ASBR in the link-state ID field.
- Type 5 – External LSA: also known as autonomous system external LSA: The external LSAs are generated by the ASBR.
- Type 6 – Multicast LSA: Not supported and not used.
- Type 7 – External LSA: also known as not-so-stubby-area (NSSA) LSA
Sources ;
http://www.freesoft.org/CIE/Topics/89.htm
http://www.metaswitch.com/resources/what-is-open-shortest-path-first-ospf