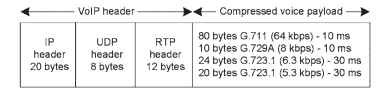
VoIP packet format with voice payload and headers
A compressed voice frame is required to be packetized with Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and IP headers and then encapsulated with network interface headers.
The RTP header is 12 bytes. Voice is sensitive to delays. RTP helps proper end-to-end delivery of real-time voice traffic. RTP header compression reduces the number of bytes, but header compression is not considered in this topic. Details on RTP are given in RFC3550.
Compressed payload, RTP, UDP, and IP header combinations are described as VoIP packets.
VoIP header = (IP + UDP + RTP) = 40 bytes in IPv4 and 60 bytes in IP version 6 (IPv6)
VoIP packet = (VoIP header + voice payload)
Physical network VoIP packet = Network interface headers + (VoIP header + voice payload)
In G.729A, 10 ms (80 samples) is the basic frame.
Voice payload varies with compression codec, payload duration, and compression rate options.
In some topics, bit rate (usually with name bandwidth) is calculated based on the VoIP packet without including the network interfaces. As an example, for G.711 of 80 bytes in a 10-ms frame, bit rate is considered as 120 bytes of 100 packets per second, (i.e., 100 x 120 x 8 = 96kbps). The actual bit rate requirements are more than 96 kbps on physical interfaces.
Codec Bit Rate (Kbps) Based on the codec, this is the number of bits per second that need to be transmitted to deliver a voice call. (codec bit rate = codec sample size / codec sample interval).
Codec Sample Size (Bytes) Based on the codec, this is the number of bytes captured by the Digital Signal Processor (DSP) at each codec sample interval. For example, the G.729 coder operates on sample intervals of 10 ms, corresponding to 10 bytes (80 bits) per sample at a bit rate of 8 Kbps. (codec bit rate = codec sample size / codec sample interval).
Codec Sample Interval (ms) This is the sample interval at which the codec operates. For example, the G.729 coder operates on sample intervals of 10 ms, corresponding to 10 bytes (80 bits) per sample at a bit rate of 8 Kbps. (codec bit rate = codec sample size / codec sample interval).
MOS MOS is a system of grading the voice quality of telephone connections. With MOS, a wide range of listeners judge the quality of a voice sample on a scale of one (bad) to five (excellent). The scores are averaged to provide the MOS for the codec.
Voice Payload Size (Bytes) The voice payload size represents the number of bytes (or bits) that are filled into a packet. The voice payload size must be a multiple of the codec sample size. For example, G.729 packets can use 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, or 60 bytes of voice payload size.
Voice Payload Size (ms) The voice payload size can also be represented in terms of the codec samples. For example, a G.729 voice payload size of 20 ms (two 10 ms codec samples) represents a voice payload of 20 bytes [ (20 bytes * 8) / (20 ms) = 8 Kbps ]
PPS PPS represents the number of packets that need to be transmitted every second in order to deliver the codec bit rate. For example, for a G.729 call with voice payload size per packet of 20 bytes (160 bits), 50 packets need to be transmitted every second [50 pps = (8 Kbps) / (160 bits per packet) ]